Describe Solids Liquids and Gases Using the Kinetic Theory
Density compressibility diffusion C11-1-02 Use the Kinetic Molecular Theory to explain properties of gases. This is also why solids are difficult to compress.
The Kinetic Theory Of Gases Kinetic Energy Of A Molecule
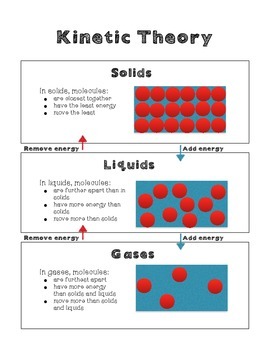
The particles in solids liquids and gases have different amounts of energy.

. Identify the molecular behavior responsible for each property of gases liquids and solids. The Kinetic Theory of Matter states that all matter is composed. Key Points All particles have energy and the energy varies depending on the temperature the sample of matter is in which determines if the substance is a solid liquid or gas.
The kinetic molecular theory is a simple but very effective model that effectively explains ideal gas behavior. Solid liquid and gas and how matter can change from one phase to another. There are energy changes when changes in state occur.
32 The kinetic molecular theory ESAAL The kinetic theory of matter helps us to explain why matter exists in different phases ie. 3- Why cant the kinetic molecular theory be applied to liquids and solids. Apr 30 2015.
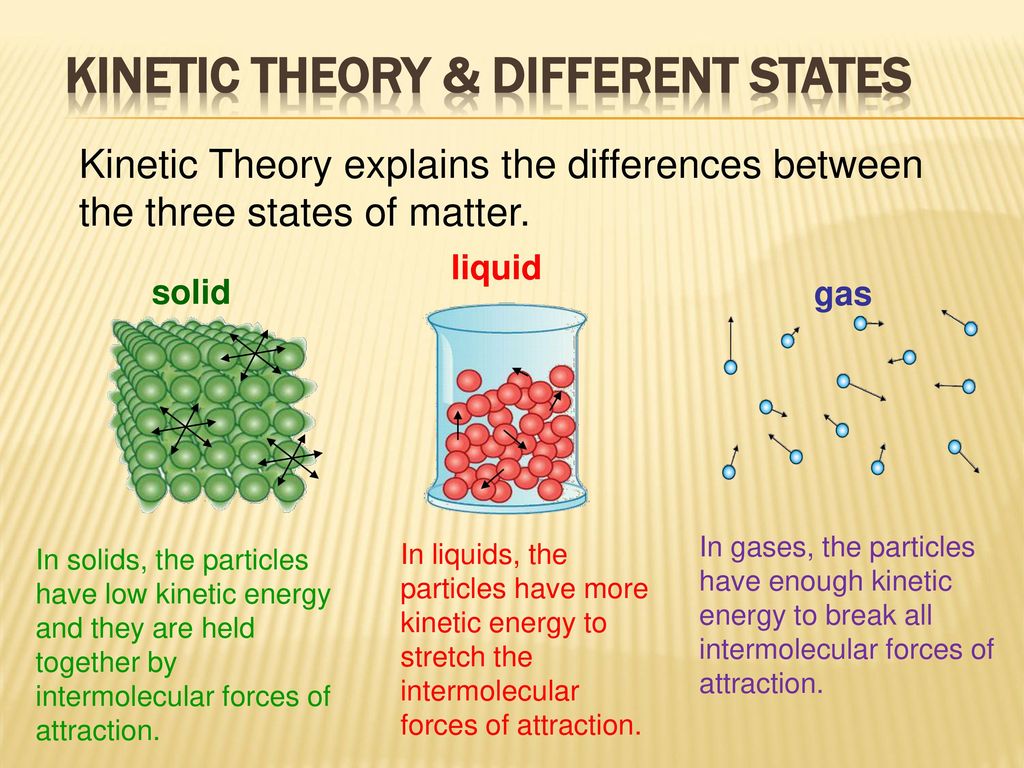
Read page 420. The particles of a solid will possess only a small amount of kinetic energy. Of or relating to motion.
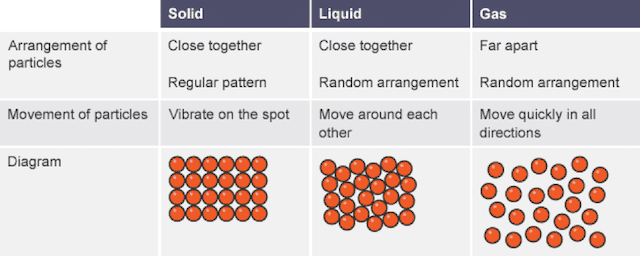
Little or no intermolecular forces. Solids Liquids Gases Volume definite or indefinite Molecular Motion high med low Distance Between Molecules 2 Read p. We will describe these by their general motion and amounts of kinetic energy as follows.
According to the basic assumption of kinetic molecular. 1 Describe how gases liquids and solids compare using the following table. HELP WITH MY HOMEWORK PLEASE.
3 Identify each statement as True or False. Use the editor to format your answer Question 3 1 Point What. Describe kinetic molecular theory.
Kinetic molecular theory is useful in describing the properties of solids liquids and gases at the molecular level. How does the kinetic molecular theory of matter work. The kinetic theory of matter also helps us to understand other properties of matter.
1- Describe the 4 standards that gases need to have in order to fit the kinetic molecular theory of gases. 2- Identity which of these gases exhibit non-ideal gas behavior. In your answer you should describe the.
What is kinetic energy. Theory of treating samples of matter as a large number of small particles atoms or molecules all of which are in constant random motion. C11-1-01 Describe the properties of gases liquids solids and plasma.
GCSE Kinetic particle theory and state changes The kinetic particle theory explains the properties of solids liquids and gases. Solid particles have the least amount of energy and gas particles have the greatest amount of energy. They are arranged differently and.
Draw clear diagrams that accurately describe how the particles are arranged in a solid a liquid and a gas. Identify each statement as True or False. Broadly the kinetic theory of matter says that all matter is composed of particles.
Describe the kinetic molecular theory of matter. The kinetic particle theory explains the properties of the different states of matter. A regular spacing or arrangement of atomsmolecules within a crystal.
The theory assumes that gases consist of widely separated molecules of negligible volume that are in constant motion colliding elastically with one another and the walls of their container with average velocities determined by their absolute temperatures. Describe the characteristic properties that differentiate gases liquids and solids. 4- Describe how surface area.
The kinetic molecular theory of matter says that molecules of gases undergo greater rotational translational and vibrational motion than the molecules solids and liquids. Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids Learning Competencies a. Gases have the most kinetic energy as a result they float around in the air.
Solids have the lowest kinetic energy as they are tightly packed and vibrate in place. Chemistry questions and answers. After kinetic theory the theories for real gases have been given with large number of empirical inter molecular potential energy functions.
Describe how gases liquids and solids compare using the following table. Describe kinetic molecular theory. 1 Solids have a definite shape and volume because solids shows that the force of attraction between the entities in the solid are very strong.
Use the editor to format your answer Question 2 1 Point Describe the 4 standards that gases need to have in order to fit the kinetic molecular theory of gases. Describe kinetic molecular theory. Solids Liquids Gases Volume definite or indefinite Molecular Motion high med low Distance Between Molecules g 2.
Their molecules just move around carelessly for as much space is available. Identify each statement as True or False. Now explain how the particles are arranged in a solid a liquid and gas using words.
Thats why gases dont have fixed volumes. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need. Solids Liquids Gases Volume definite or indefinite Molecular Motion high med low Distance Between Molecules g 2.
What is kinetic energy. The kinetic theory is applicable to gases with low density at high temperatures. KMT is most often referenced in relation to the behavior of.
What is kinetic energy. The force of attraction also is the reason why solids are close together. Kinetic Molecular Theory Definition KMT Kinetic Molecular Theory KMT describes the experimentally discovered behavior of particles.
Liquids have comparatively higher kinetic energy so the particles slide past each other. Describe how gases liquids and solids compare using the following table. According to the basic assumption of kinetic.
Question 1 1 Poin Why cant the kinetic molecular theory be applied to liquids and solids. The imaginary gas that obeys all assumptions in kinetic theory of gases is known as ideal gas. Chemistry questions and answers.
Describe and differentiate the types of intermolecular forces. 2 Gases are relatively easy to compress while solids are virtually. A component in a material system that is distinguished by chemical composition andor physical.
Random motion intermolecular forces.
States Of Matter Book Energy And Matter
No comments for "Describe Solids Liquids and Gases Using the Kinetic Theory"
Post a Comment